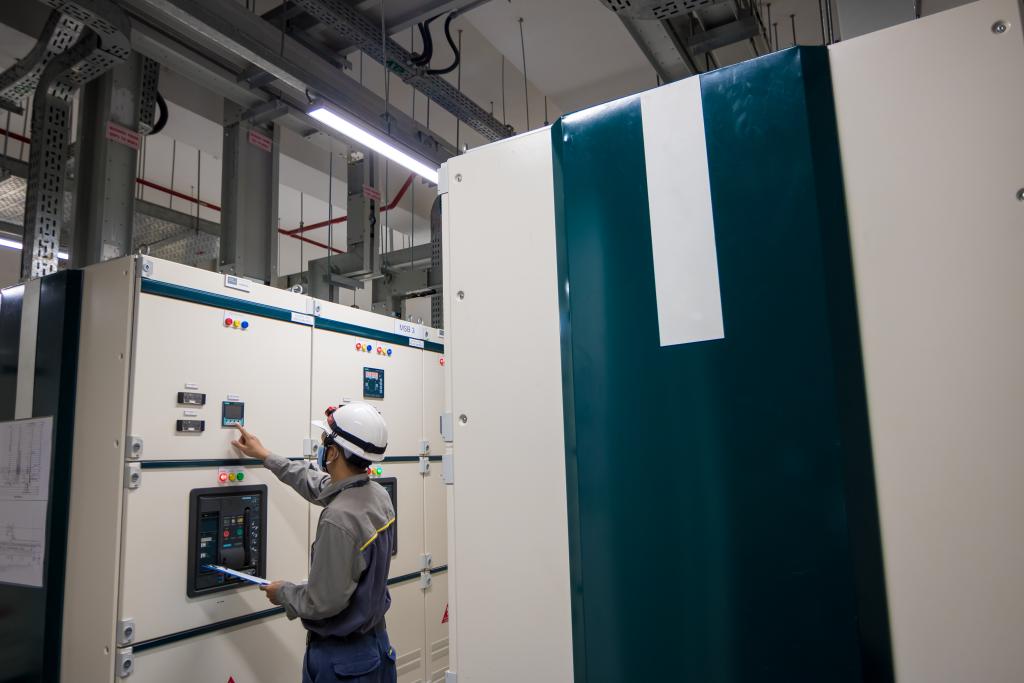
Maintenance is a regular practice that technicians perform to ensure system efficiency and reliability. Many types of maintenance strategies have been introduced and successfully implemented. They are divided into 3 main categories: Reactive Maintenance, Proactive Maintenance, and Total Productive Maintenance. Each of them has its own set of maintenance strategies with different pros and cons. But which one is considered the best maintenance strategy?

Key Takeaways
-
- What types of maintenance are there?
- Which one is the best maintenance strategy?
Reactive Maintenance
Reactive Maintenance is repairing assets to normal operating conditions after discovering poor performance or breakdown. Lower costs and less staff requirement are the primary benefits of this type of maintenance. Reactive maintenance includes:
Breakdown Maintenance
Breakdown Maintenance is a set of actions taken when machinery is completely broken and may require extensive repairs (or may need to be replaced entirely) to run again.

Run-to-failure maintenance
Run-to-failure Maintenance is deliberately allowing a machine to run until it breaks down, with the condition the breakdown does not pose a health or safety risk to operating personnel.

Corrective maintenance (CM)
Corrective Maintenance is any task that targets and repairs an asset malfunction to resume it to proper working order. The actions can be planned or unplanned.
Emergency maintenance
Emergency Maintenance is the last-minute response when an asset experiences a sudden breakdown that can cause considerable health and safety problems or big production delays.
Proactive Maintenance
Proactive Maintenance is the maintenance approach of finding underlying equipment conditions. The objective of proactive maintenance is to fix or prevent any issues in advance. Proactive Maintenance consists of:

Preventive maintenance (PM)
Preventive Maintenance is the most popular proactive maintenance strategy where maintenance work is performed at regular intervals. The intervals are either time-based (calendar-based) or usage-based.

Condition-based maintenance (CBM)
Condition-based Maintenance uses sensor devices to collect real-time measurements. The data allows maintenance personnel to perform maintenance at the exact moment it is needed, before failure.

Predictive maintenance (PdM)
Predictive Maintenance uses a combination of condition monitoring sensors and machine learning to forecast failures before they happen so maintenance can occur at just the right time.

Prescriptive maintenance (RxM)
Prescriptive Maintenance uses prescriptive analytics to perform self-diagnosis and present technicians with multiple scenarios, and alternatives on how to deal with the identified issue(s).
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) is a holistic approach that operates with the idea that everyone in a facility should participate in maintenance rather than just the maintenance team. This approach utilizes the knowledge and skills of all employees, into the everyday performance of a facility.
This approach strives to achieve perfect production, including no breakdowns, small stops or slow running, defects, or accidents.
Among the listed above maintenance strategies, Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) seems to be the optimal maintenance strategy. However, depending on industry sectors, asset value, budget, personnel skill sets, and company culture, maintenance strategies are different between organizations.
We believe that the best maintenance approach is to apply a combination of maintenance strategies, based on the current capabilities and limitations of the organization as well as the condition, performance, and importance of used assets.





